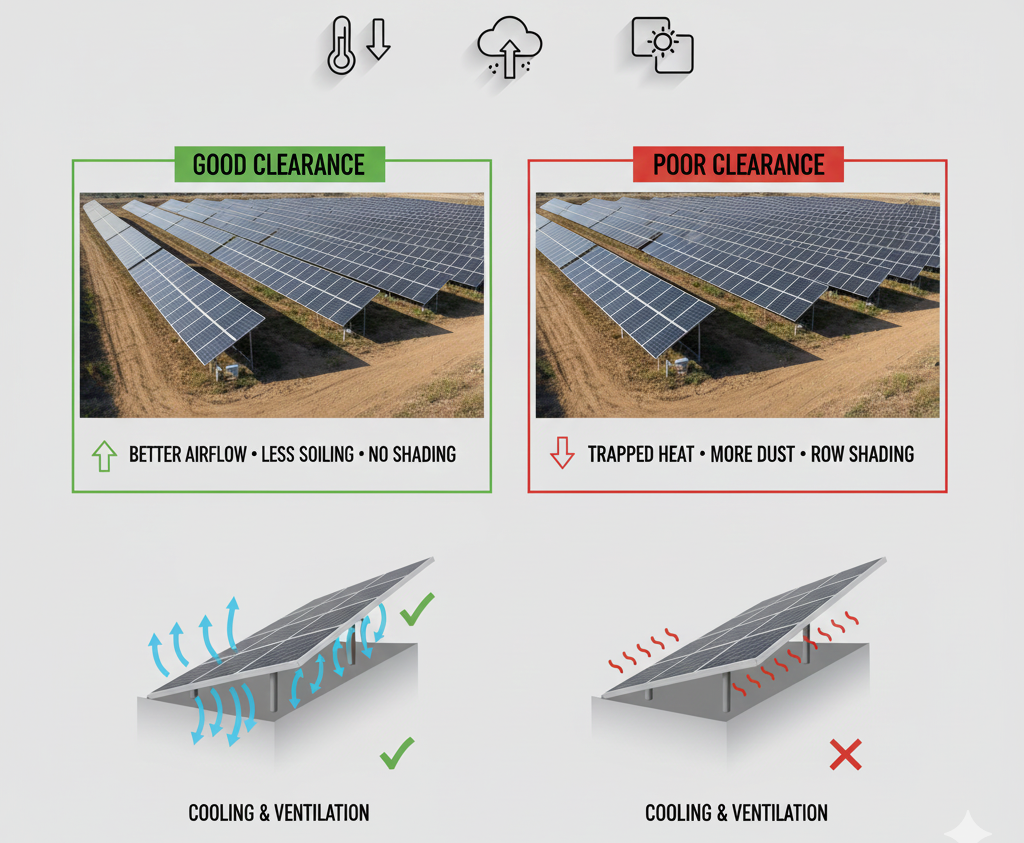
When engineering a large-scale Photovoltaic (PV) power plant, the focus often centers on the solar panels and high-tech inverters. However, a less obvious detail—clearance (the precise vertical space between the solar modules and the ground, and horizontal spacing between rows)—is a critical factor that directly controls long-term performance, efficiency, and operational costs.
The Hidden Performance Drivers of PV Clearance
Choosing the correct clearance impacts four essential areas of solar farm profitability:
1. Thermal Management & Cooling
Solar panels lose efficiency when they overheat. Without adequate ground clearance, heat is trapped beneath the modules, severely restricting natural airflow and ventilation. In hot climates, proper spacing can significantly enhance cooling, thereby preventing performance degradation and boosting energy output by several percentage points.
2. Minimizing Soiling and Snow Loss
Panels installed too close to the ground are susceptible to environmental factors that reduce output:
- Soiling: Low installation heights increase the collection of wind-blown dust, sand, and mud splashes, accelerating module degradation and necessitating more frequent, costly cleaning cycles.
- Snow Accumulation: In cold regions, insufficient clearance means snow cannot slide off easily or melt from the module’s edge, leading to prolonged energy production loss.
3. Preventing Inter-Row Shading
Clearance directly influences the required row spacing. If panels are positioned too closely or too low, one row will cast shadows onto the next, particularly during winter when the sun’s path is low. Even minor shading dramatically reduces energy harvest across the affected modules.
4. Operational Efficiency and Safety
Sufficient height and spacing are vital for site Operations and Maintenance (O&M). Optimal clearance provides safe, easy access for technicians to inspect wiring, maintenance equipment, and mounting structures, reducing labor time and minimizing the risk of accidental component damage.
Finding the PV Clearance Sweet Spot
The ideal clearance is not uniform; it is a complex balance determined by several variables: local climate, specific soil type, regulatory codes, panel tilt angle, and potential wind loads.
While insufficient clearance causes overheating, shading, and soiling, excessive height increases structural material costs and exposes the system to higher wind stress. The goal is an optimized clearance design that maximizes solar energy capture while maintaining structural and budgetary efficiency.
Conclusion: Strategic clearance design is a cornerstone of PV system reliability. By optimizing ventilation, mitigating soiling, and ensuring safe maintenance access, solar developers ensure their power plant operates at its peak efficiency, delivering maximum return on investment.
